Miyawaki
Miyawaki TB7N Temperature Control Steam Trap

Manufacturer: MIYAWAKI Inc.
Model: TB7N
Features
Complete steam containment
The temperature control trap operates with an adjustable subcooling of condensate. Thus maintaining a certain condensate level in the trap. This mechanism provides a 100% tight sealing and effectively prevents steam loss during operation.
Superb durability
The MIYAWAKI SCCV (Self Closing and Centering Valve) System has the effect of increasing durability by achieving soft closing during operation.
Consisting of a free rotating valve that is centered and guided by the condensate flow, hence perfectly fitted in the valve seat even under extreme conditions of high pressure applications. This significantly reduces wear and erosion of the valve components.
Quick startup
Swiftly discharges the initial cold condensate and air.
Also fulfils the function of an air vent.
Energy saving effect
A significant energy saving effect is achieved by controlling the temperature of discharged condensate. Especially in application where sensible heat of condensate can be used for heating purpose, this trap reduces steam consumption significantly.
Optional: blowdown valve
Also available are versions with a blowdown valve to eliminate dirt from pipelines and scale without having to disassemble the trap.
If you require a a blowdown valve, please specify TB7BN-C or TB7BN-R.
● select TB7BN-C up to 0,98MPa (142psig)
● select TB7BN-R up to 2,1MPa (305psig)
Typical applications
Suitable for steam main lines, trace lines, and other such applications.
Dimensions/Weight
Screwed / Socket Weld
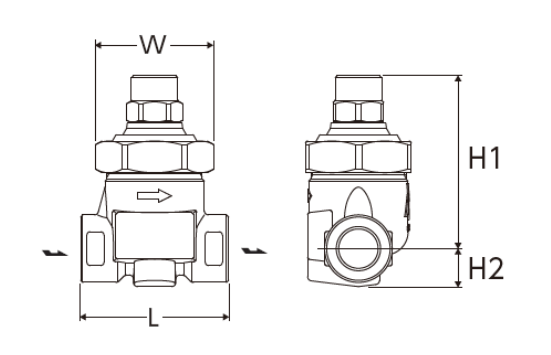
| Size | Dimensions (mm) | Dimensions (in) | Weight | |||||||
| L | H1 | H2 | W | L | H1 | H2 | W | (kg) | (lb) | |
| 1/2” | 70 | 82 | 18 | 56 | 2.8 | 3.2 | 0.7 | 2.2 | 0,9 | 2.0 |
| 3/4” | 80 | 19 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 1,0 | 2.2 | ||||
| 1” | 23 | 0.9 | 1,1 | 2.4 | ||||||
Flanged
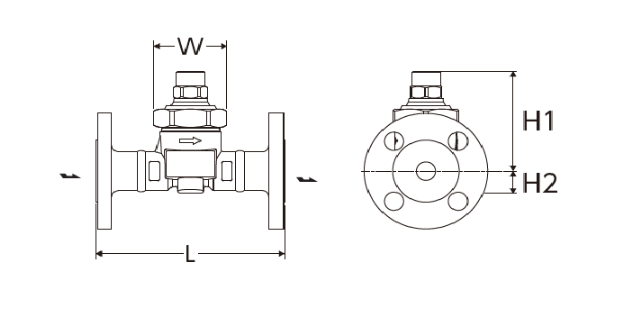
JIS,ASME
| Size | Dimensions (mm) | Dimensions (in) | Weight (kg) | Weight (lb) | ||||||||||||||
| L | H1 | H2 | W | L | H1 | H2 | W | JIS(FF,RF) | JIS(RF) | ASME/JPI(RF) | JIS(FF,RF) | JIS(RF) | ASME/JPI(RF) | |||||
| 10K,16K | 20K | 30K | 150lb | 300lb | 10K,16K | 20K | 30K | 150lb | 300lb | |||||||||
| 1/2” | 145 | 82 | 18 | 56 | 5.7 | 3.2 | 0.7 | 2.2 | 2,4 | 2,5 | 2,6 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 5.3 | 5.5 | 5.7 | 4.4 | 5.5 |
| 3/4” | 19 | 0.8 | 2,8 | 2,9 | 3,0 | 2,5 | 3,4 | 6.2 | 6.4 | 6.6 | 5.5 | 7.5 | ||||||
| 1” | 23 | 0.9 | 3,9 | 4,1 | 4,2 | 3,2 | 4,2 | 8.6 | 9.0 | 9.2 | 7.0 | 9.2 | ||||||
DIN PN40
Size | Dimensions (mm) | Dimensions (in) | Weight | |||||||
| L | H1 | H2 | W | L | H1 | H2 | W | (kg) | (lb) | |
| DN15 | 150 | 82 | 18 | 56 | 5.9 | 3.2 | 0.7 | 2.2 | 2,6 | 5.7 |
| DN20 | 3,4 | 7.5 | ||||||||
| DN25 | 160 | 6.3 | 4,0 | 8.8 | ||||||
*Customized face-to-face dimensions on request.
*Please contact MIYAWAKI for further information.
Specifications
| Model | Connection | Max. operating pressure | Max. operating pressure differential | Max. operating temperature | Adjustable range | Standard set temperature | Body material | ||||||
| Type | Size | PMO (MPa) | PMO (psig) | (MPa) | (psig) | TMO (℃) | TMO (℉) | (℃) | (℉) | (℃) | (℉) | ||
| TB7N | Screwed Rc,NPT | 1/2” | 2,1 | 305 | 2,1 | 305 | 350 | 662 | 50 – 200 | 122 – 392 | 100 (at 1,0MPa) | 212 (at 145psig) | Forged steel A105 |
| 3/4” | |||||||||||||
| 1” | |||||||||||||
| TB7NF | Flanged FF,RF | 1/2” | |||||||||||
| 3/4” | |||||||||||||
| 1” | |||||||||||||
| TB7NW | Socket Weld SW | 1/2” | |||||||||||
| 3/4” | |||||||||||||
| 1” | |||||||||||||
Maximum allowable pressure (PMA): 4,0MPa (580psig) PMA is the pressure that can be tolerated by pressure-resistant parts (body).
Maximum allowable temperature (TMA): 400℃ (752℉) TMA is the temperature that can be tolerated by pressure-resistant parts (body).
Minimum operating differential pressure (⊿PMN): 0,01MPa (1.5psig) ⊿PMN is the minimum operating differential pressure between the trap inlet and outlet.
*It is possible to change the standard factory set temperature. Please specify the operating pressure and set temperature.
*Please refer to the installation manual how to adjust the set temperature.
Discharge Capacity
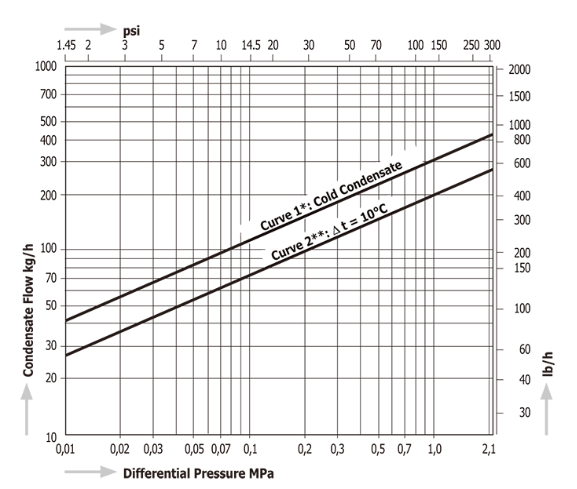
⊿t is the difference between the temperature of a temperature control trap when the valve is initially opened and condensate temperature. The temperature difference (⊿t) upon the initial passage of air is great, and indicates that the flow rate will also increase.
* Curve1 shows the trap’s maximum capacity when discharaging cold condensate.
**Curve2 shows the trap’s maximum capacity when discharaging hot condensate at a temperature of 10°C (18°F) below the adjusted temperature of the trap.
Installation Examples