Fushiman Co.
Fushiman GH5 type/GH5M type temperature control valve
Manufacturer: Fushiman Co.,LTD.
Model: GH5
| Model | Nominal diameter | Pressure | Temperature setting | Body Material | Connection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH5 | 20-32 | Max. 0.4MPa | 25 to 60°C | CAC | Screw in |
- Made of CAC and stainless steel (SUS), this compact and lightweight three-way valve is ideal for integration into equipment.
Improved from the conventional GH5-20 model, with expanded size variations.
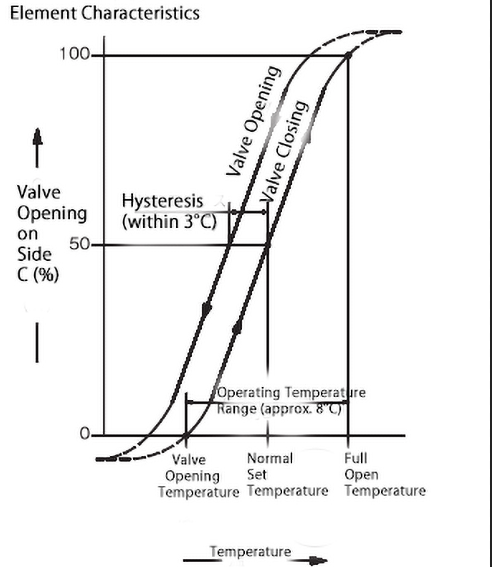
The GH5 and GH5M models are automatic temperature control valves using a wax element
The GH5 model can be used for temperature control in the circulation line of the TFR3 hot water production system (see page 172), as well as for temperature regulation of small-scale cooling systems.
Features
- Compact, lightweight, and affordable.
Excellent responsiveness.
Reduced valve seat leakage.
Applicable to both diverting and mixing types.
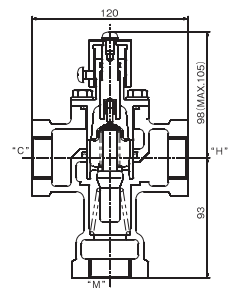
Structure and Dimensions
Specifications
| Model | Diverting Type: GH5 Model, Mixing Type: GH5M Model | ||||
| Fluid | Chilled/hot water, antifreeze liquid, and other non-corrosive fluids | ||||
| Nominal Diameter | 20、25、32 | ||||
| Operating Pressure | Up to 0.4MPa | ||||
| Differential Pressure (Across Valve) | Súp tổ 0.25MPa | ||||
| Set Temperature | 25-30-35-40-45-50-55-60℃ | ||||
| Temperature Resistance of Element | Set temperature +30°C (for a short time) | ||||
| Valve Seat Leakage | 1 liter/min or less (at a differential pressure of 0.1 MPa) | ||||
| Maximum Flow Rate, Cv Value | Nominal Diameter | 20 | 25 | 32 | |
| Maximum Flow Rate (ℓ/min) | 55 | 85 | 120 | ||
| Cv Value | 5.5 | 7 | 10 | ||
| Material | Valve Body | Bronze | |||
| Element | Bronze, stainless steel, etc. | ||||
| Spring | Stainless steel | ||||
| Pipe Connection | Threaded (JIS Rc) | ||||
| Weight | 2.7kg | ||||
Note: When used for circulation in a TFR3-type hot water production system, it may be referred to as a GH5-type thermostat.
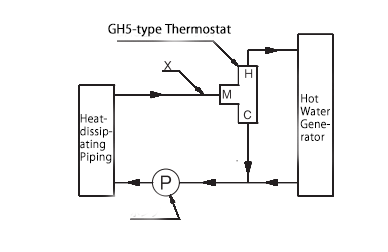
Installation Example (Control Method Example)
Control Method: Diverting type (when used with a TFR3-type hot water production unit)
This method controls the flow to the hot water production unit based on the temperature of the fluid entering point M, keeping the temperature at point X constant.
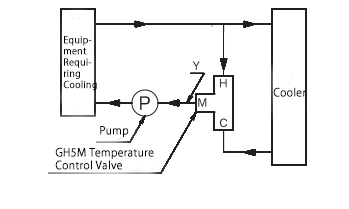
○Control Method: Mixing Type
This method adjusts the mixing ratio between the fluid entering point H and the cooled fluid passing through the cooler, in order to maintain a constant temperature at point Y.