Nippon Yakin Kogyo Co., Ltd
Nippon Yakin Kogyo NAS335X Corrosion Resistant Alloys


Manufacturer: Nippon Yakin Kogyo Co., Ltd
Model: NAS335X
Stainless steel alloys like JIS-UNS N08020 DIN/EN-NAS335X offer exceptional corrosion resistance to sulfuric acid, making them ideal for harsh chemical environments. These alloys perform well in high-concentration sulfuric acid and elevated temperatures, providing durability and protection against intergranular corrosion and stress corrosion cracking. They ensure long-lasting efficiency for industries facing aggressive chemical exposure.
| Chemical Composition | 20Cr-33Ni-2.5Mo-3Cu-0.4Nb | ||
| Product Shape |
|  Sheet Sheet |
Plate |
| Workability | Cold and hot workability are approximately equal to those of Type 304, 316, and other standard austenitic stainless steels. | ||
| Weldability | TIG welding, MIG welding, and shielded metal arc welding apply in the same manner as with standard austenitic stainless steels.It is recommended to use ER320 or ER320LR welding electrodes..However, reduce welding heat input as far as possible for Nb-added stainless steel. | ||
| Machinability | Machinability is similar to that of standard austenitic stainless steels. A machinist should use a high-speed steel tool or an ultrahard tool. Additionally, it is recommended to adopt a slower feed rate and a deeper cutting depth | ||
| Heat Treatment | Stabilizing heat treatment should be performed at a temperature range from 925°C to 1010°C, followed by quenching in water or rapid cooling by other means. (Conditions provided in ASTM A480/A480M). | ||
| Pickling | Pickling is performed under the same conditions as with Type 304, using a mixture of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid. | ||
| Applications | Chemical plants, heat exchangers, sulfuric acid-related equipment. | ||
Steel Grade/Standard
| Nippon Yakin Grade | JIS G 4902 | ASTM A240/B463 | EN |
| NAS335X | NCF020 | UNS N08020 | — |
Chemical Composition
| Specification | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Mo | Cu | Nb |
| NCF020 | ≤0.07 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.035 | 32.00-38.00 | 19.00-21.00 | 2.00-3.00 | 3.00-4.00 | 8xC-1.00 |
| ASTM A240 | ≤0.07 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.035 | 32.00-38.00 | 19.00-21.00 | 2.00-3.00 | 3.00-4.00 | 8xC-1.00 |
| ASTM B463 | ≤0.07 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.035 | 32.00-38.00 | 19.00-21.00 | 2.00-3.00 | 3.00-4.00 | 8xC-1.00 |
Physical Properties
| Density [g/cm³] | 8.08 |
| Specific heat [J/kg·K] | 470 |
| Electrical resistivity [µΩ·cm] | 105 |
| Thermal conductivity [W/m·K] | 11.4 |
| Average coefficient of thermal expansion [10⁻⁶/°C] | 10–100°C: 14.6 20–200°C: 15.9 20–300°C: 15.8 20–400°C: 16.0 |
| Young’s modulus [MPa] | 18.9 x 10³ |
| Magnetism | None |
| Melting range [°C] | 1340–1389 |
Mechanical Properties
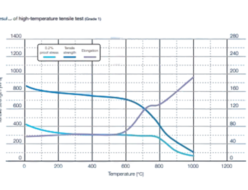
Mechanical Properties at Room Temperature
| 0.2% proof stress [MPa] | Tensile strength [MPa] | Elongation [%] | Hardness [HBW] | |
| Specification (NCF020) | ≥240 | ≥550 | ≥30 | ≥217 |
| Specification (ASTM A240) | ≥240 | ≥550 | ≥30 | ≥217 |
| Cold-rolled sheet 2.0mm | 431 | 698 | 38 | 176 |
| Hot-rolled plate 6.5mm | 359 | 686 | 40 | 137 |
| Hot-rolled plate 50mm | 315 | 581 | 42 | 156 |
Corrosion Resistance
NAS335X contains high levels of Ni, Mo, and Cu, which provide it with excellent resistance to sulfuric acid. Furthermore, as a low carbon, Nb-added material, it also demonstrates outstanding intergranular corrosion resistance.Its combination of resistance to sulfuric acid and intergranular corrosion makes NAS335X an ideal material for challenging environments.
Pitting Corrosion Resistance
| Alloy | ASTM G48 Method A | ASTM G48 Method C Critical Pitting Corrosion Temperature CPT (°C) | |
| 22°C | 50°C | ||
| SUS316L | ✖ | ✖ | — |
| NAS64 | ◯ | ◯ | 55 |
| NAS254N | ◯ | ◯ | 80 |
| NAS335X | ◯ | ◯ | 85 |
Test Conditions
ASTM G48 Method A: No Pitting Corrosion.
– Test Solution: 6% FeCl3, 72h
ASTM G48 Method C: 6% FeCl3 + 1% HCl, 72h
Crevice Corrosion Resistance
| Alloy | ASTM G48 Method D Critical Crevice Corrosion Temperature CCT (°C) |
| SUS316L | <10 |
| NAS64 | 30 |
| NAS254N | 45 |
| NAS335X | 55 |
Test Conditions
ASTM G48 Method D: Critical crevice corrosion temperature test.
– Test Solution: 6% FeCl3 + 1% HCl, 72h
Acid Resistance
| Alloy | Corrosion rate in sulfuric acid at 80°C (mm/y) | |||||
| 5% | 10% | 20% | 40% | 60% | 80% | |
| SUS316L | 1.67 | 4.69 | 7.191 | 24.90 | 70.45 | 33.74 |
| NAS64 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 1.07 | 19.19 | 1054 | 60.72 |
| NAS254N | 0.02 | 0.05 | 1.2 | 2.16 | 7.76 | — |
| NAS335X | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 2.15 |
Test time: 24h
| Alloy | Corrosion rate in boiling sulfuric acid (mm/y) | |||
| 5% | 10% | 20% | 40% | |
| SUS316L | 8.19 | 24.61 | 17.89 | 3129 |
| NAS64 | 0.35 | 1.65 | 17.68 | 4829 |
| NAS254N | 1.17 | 3.30 | 7.90 | 24.65 |
| NAS335X | 0.44 | 0.68 | 0.52 | 2.64 |
Test time: 24h
(Reference)
| Alloy | JIS | UNS No. | Chemical Composition |
| SUS316L | SUS316L | S31603 | 17Cr-12Ni-2Mo |
| NAS64 | SUS329J4L | S32605 | 25Cr-6.5Ni-3.3Mo-0.17N |
| NAS254N | SUS836L | S32053 | 23Cr-25Ni-5.5Mo-0.2N |
| NAS335X | NCF020 | N08020 | 20Cr-33Ni-2.5Mo-3Cu-0.4Nb |
Workability
NAS335X offers the same hot and cold workability as standard austenitic stainless steels. Moreover, you can easily work with NAS335X under both hot and cold conditions, and at the same time maintain its excellent formability in various environments.
Weldability
Moreover, you can easily work with NAS335X under both hot and cold conditions, and at the same time maintain its excellent formability in various environments. To achieve optimal welding performance, use ER320 or ER320LR welding electrodes, ensuring the best results for welding NAS335X.
Machinability
NAS335X offers machinability similar to standard austenitic stainless steels. Moreover, for better machinability, using a high-speed steel tool or an ultrahard tool is recommended. Additionally, applying a slower feed rate and a deeper cutting depth ensures optimal results during machining.
Heat Treatment
To perform the stabilizing heat treatment of NAS335X, heat it within the temperature range of 925°C to 1010°C. After heating, quench it in water or rapidly cool it by other means, as outlined in ASTM A480/A480M..
Pickling
Perform pickling under the same conditions as for Type 304 stainless steel. Specifically, use a mixture of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid for this process to ensure optimal results. By following these steps, you maintain the same effectiveness as when working with Type 304 stainless steel
Applications
NAS335X is commonly used in chemical plants, heat exchangers, and sulfuric acid-related equipment. Thus, its superior resistance to sulfuric acid makes it ideal for these industrial applications.
Related Products
-

Nippon Yakin Kogyo NAS74N Corrosion Resistant Alloys
-

Nippon Yakin Kogyo NAS8R10 Neutron Absorbing Stainless Steel
-

Nippon Yakin Kogyo NASPB SoftMagnetic Alloys
-
Nippon Yakin Kogyo NAS625 Corrosion Resistant Alloys
-

Nippon Yakin Kogyo NAS631 High Strength Stainless Steels
-

Nippon Yakin Kogyo NASNW400 Corrosion Resistant Alloys