Nippon Yakin Kogyo Co., Ltd
Nippon Yakin Kogyo NAS600 Heat Resistant Alloys



Manufacturer: Nippon Yakin Kogyo Co., Ltd
Model : NAS600
NAS600 (UNS N06600)
Heat-Resistant Nickel Alloy
NAS600 (NCF600, UNS N06600) is a nickel-chromium alloy that provides excellent resistance to oxidation at high temperatures. Nippon Yakin supplies this product in plate, sheet, and strip forms.
| Chemical Composition | 77Ni-16Cr-6Fe | ||
| Product Shape |  Coil Coil |  Sheet Sheet |  Plate Plate |
| Workability | Hot working is relatively easy with NASH600. For hot working, the temperature should be between 1000°C and 1150°C, although light work may be done at 850°C. Cold workability is easier than austenitic stainless steels, similar to Monel. | ||
| Weldability | As with standard austenitic stainless steels, NASH600 may be welded using techniques such as TIG, MIG, and shield metal arc welding. For edge preparation, mechanical cutting is advisable. | ||
| Heat Treatment | The following heat treatments may be used: – Annealing: 800–150°C; Air or water cooling. | ||
| Machinability | As a high nickel alloy, NASH600 is not as machinable as an austenitic stainless steel. We may use a high-speed cutting tool, though we recommend a sintered carbide tool. The recommended feed speeds are as follows: – High-speed steel tool: 100–135m/min – Sintered carbide tool: 300–250m/min. -You should completely remove lubricants after machining before welding or heat treating. | ||
| Properties at High Temperatures | Engineers rely on NASH600 for its particularly superior oxidation resistance at high temperatures, which allows them to use it continuously in air and other environments for extended periods. Additionally, due to its excellent resistance to nitrogen, hydrogen, and carburization, engineers frequently use NASH600 in heat treatment furnaces. However, caution is necessary when dealing with chlorine and bromide, as these substances can cause damage. – Long-term continuous use in air oxidizing environment: 1100°C – Reducing environment of H2 or CO not containing sulfur: 1150°C – Excluding sulfur environment (in air containing sulfuric acid): 815°C – Reducing environment containing hydrogen sulfide: 535°C | ||
| Applications | Heat treatment fixtures, Muffle furnace, Chemical plants. | ||
Grade/Standard
| Nippon Yakin Grade | JIS G 4902 | ASTM | EN |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAS600 | NCF600 | UNS N06600 | 2.4816 |
Chemical Composition
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Cu | Al | Ti | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specification (NCF600) | ≤0.15 | ≤0.50 | ≤1.00 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.015 | ≥72.00 | 14.00–17.00 | ≤0.50 | — | — | 6.00–10.00 |
| Specification (UNS N06600) | ≤0.15 | ≤0.50 | ≤1.0 | — | ≤0.015 | ≥72.00 | 14.00–17.00 | ≤0.50 | — | — | 6.00–10.00 |
| Specification (EN 2.4816) | 0.05–0.10 | ≤0.50 | ≤1.00 | ≤0.020 | ≤0.015 | ≥72.00 | 14.00–17.00 | ≤0.50 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.30 | 6.00–10.00 |
Physical Properties
| Density [g/cm³] | 8.51 |
| Specific heat [J/kg•K] | 444 |
| Electrical resistivity [μΩ•cm] | 92.5 |
| Thermal conductivity [W/m•K] | 12.3 |
| Average coefficient of thermal expansion [10⁻⁶/°C] | 25–93°C 13.3 |
| 25–316°C 14.2 | |
| 25–538°C 15.1 | |
| 25–760°C 16.0 | |
| 25–982°C 16.7 | |
| Young’s modulus [MPa] | 21.4 × 10⁴ |
| Curie point [°C] | −124 |
| Magnetism [μ] | None |
| Melting range [°C] | 1370–1410 |
Mechanical Properties
Mechanical Properties at Room Temperature
| Specification | Mechanical Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2% proof stress [MPa] | Tensile strength [MPa] | Elongation [%] | Hardness | |
| Specification (NCF600) | ≧245 | ≧550 | ≧30 | ≦182 |
| Specification (UNS N06600) | ≧240 | ≧550 | ≧30 | — |
| Specification (EN 2.4816) | ≧240 | 500-850 | ≧30 | ≦200 |
| Hot-rolled plate | 321 | 677 | 42 | 171 |
| Cold-rolled sheet | 337 | 704 | 40 | 84 (HRBW) |
High Temperature Strength
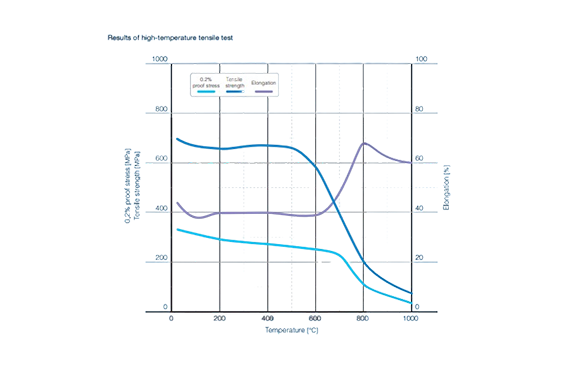
Creep Properties
| Heat treatment | Temperature [°C] | Creep rupture strength [MPa] |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing (Cold-rolled sheet) | 538 | 511 |
| 649 | 234 | |
| 760 | 89 | |
| 871 | 52 |
Corrosion Resistance
The composition of NAS600 provides corrosion resistance in a remarkably large number of corrosive environments. The addition of chromium content provides superior corrosion resistance in acidic environments over pure nickel. Furthermore, the high nickel content maintains the corrosion resistance in a reducing state and exhibits superior corrosion resistance to alkaline solutions. Another feature of this product is the high level of resistance against stress corrosion cracking.
Comparison of Alloys in Stress Corrosion Cracking Test
| Alloy | Main chemical composition (wt %) | 45% (154°C) | 42% (142°C) | 40% (138°C) | 38% (134°C) | 35% (126°C) | 30% (115°C) | 25% (110°C) | 20% (108°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 304 | 18Cr-8Ni | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Type 316L | 17Cr-12Ni-2Mo | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| NAS64 | 25Cr-6Ni-3.3Mo-0.16N | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| NAS185N | 20Cr-18Ni-6Mo-0.8Cu-0.2N | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| NAS254N | 23Cr-25Ni-5.5Mo-0.2N | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| NAS255NM | 20Cr-25Ni-6Mo-1Cu-0.2N | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| NAS354N | 23Cr-35Ni-7.5Mo-0.2N | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| NAS600 | Ni-17Cr | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| NASNW276 | Ni-15Cr-16Mo-4W-5Fe | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| NASNW22 | Ni-21Cr-13Mo-3W-4Fe | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
Workability
Hot working is relatively easy with NAS600. Operators should maintain temperatures between 1000 and 1180°C for hot working, although they can perform light work at temperatures as low as 850°C. However, they should avoid the range between 650 and 850°C, as cracking may occur. Cold workability is easier than austenitic stainless steels, similar to Monel.
Weldability
You can weld NAS600 using techniques such as TIG, MIG, and shielded metal arc welding, just like with standard austenitic stainless steels. For edge preparation, it is desirable to use mechanical cutting. Additionally, operators should use wide U- and V-groove angles.Care should be taken to ensure its welding portion is clean as NAS600 is sensitive to surface contamination.
Heat Treatment
You may use the following heat treatment:
- Annealing: 800-1150°C; Air or water cooling.
Care should be taken at temperatures exceeding 1050°C as there is a strong tendency for the crystal grains to become coarse.
Machinability
As a high-nickel alloy, NAS600 is not as machinable as an austenitic stainless steel. A high-speed steel cutting tool may be used, though a sintered carbide tool is recommended. Also, the feed speed should be somewhat reduced, aiming for deep cutting. The recommended lathe feed speeds are as follows:
- High-speed steel tool: 1050-1350mm/min
- Sintered carbide tool: 3000-5250mm/min
After machine work, lubricants should be completely removed before welding or heat treating.
Properties at High Temperatures
Exhibiting particularly superior oxidation resistance at high temperatures, NAS600 can be used in air as well as other environments continuously for long periods of time. Because it has excellent resistance to nitrogen, hydrogen, and carburization, NAS600 can be used in heat treatment furnaces. Care is needed with wet chlorine and bromide, however, as they will cause damage.
The maximum temperatures that NAS600 may be used in different environments are as follows:
- Long-term continuous use in air oxidizing environment: 1100°C
- Reducing environment of H₂ or CO not containing sulfur: 1150°C
- Oxidizing sulfur environment (in air containing sulfurous acid): 815°C
- Reducing environment containing hydrogen sulfide: 535°C
- Hydrogen chloride: 540°C
- Chlorine gas: 510°C
Applications
- Heat treatment fixtures
- Muffe furnace
- Chemical plants
Related Products
-

Nippon Yakin Kogyo NAS255NM Corrosion Resistant Alloys
-

Nippon Yakin Kogyo NAS255 Corrosion Resistant Alloys
-

Nippon Yakin Kogyo NAS36LG Controlled Expansion Alloys
-

Nippon Yakin Kogyo NAS22-3 Controlled Expansion Alloys
-

Nippon Yakin Kogyo NASNM15M Non-Magnetic Alloys
-

Nippon Yakin Kogyo NAS36 Controlled Expansion Alloys






