Bolt & Nut, Hard Lock Nut, Japan
HARDLOCK Rim Type Nut Standard

Product: Made in Japan
Manufacturer: HARDLOCK
Basic Rim Type M5, M6, M8, M10, M12, M16, M20, M22, M24, M27, M30
HARDLOCK Nut provides unparalleled self locking performance even in the toughest environments and applications
When you need fail safe fastening performance in the most demanding vibration environment, trust HARDLOCK Nuts (HLN) to meet or exceed your expectations. 
Play will lead to not only shortened life span but also bolt brakeage which can result in catastrophic accidents.
We hit on the idea of utilizing the wedge principle, widely used in ancient Japanese architecture.
Thanks to the design inspired by the principle, HLN completely eliminates the play between the threads and withstands severe vibration longer than any other nuts in the world.
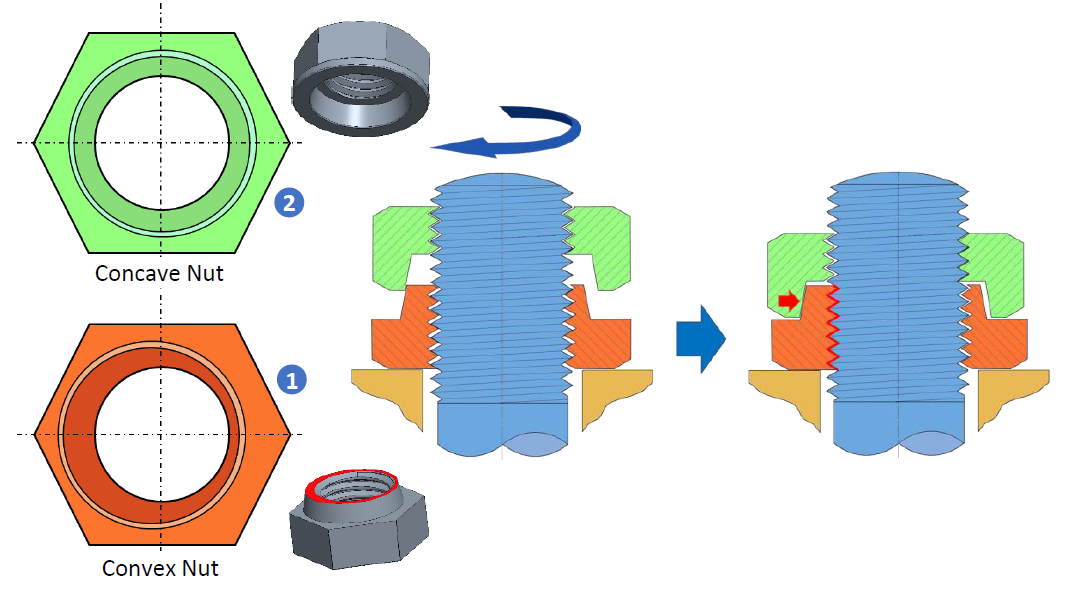
HLN consists of two nuts, the first nut 1 “Convex Nut” (clamping nut) has an eccentric protrusion on the upper surface.
The second nut 2 “Concave Nut” (locking nut) is designed with a concentric recess for locking the two nuts together.
By tightening the Concave Nut onto the Convex Nut, a strong perpendicular load will be applied to the bolt from both sides locking the HLN and making it resistant to vibrations and impacts from any direction.
After installing HLN you will realize a significant decrease in maintenance related work due to its exceptional self locking effect.
This will offer improvement of running cost, though HLN is a high end product, in combination with the advantage that it can be reused multiple times without almost any decrease in performance.
HARDLOCK NUT INSTALLATION
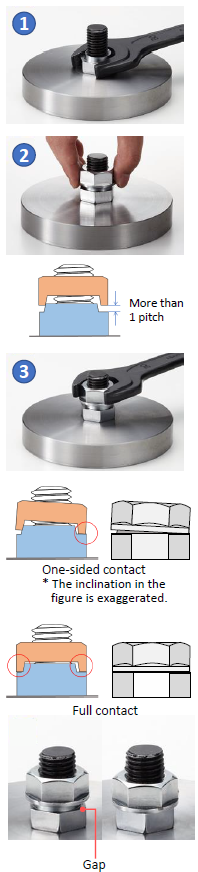
- Use a tightening tool (spanner, torque wrench etc.) to tighten the Convex Nut to the appropriate torque for the applicationThe convex nut has the same strength class as a regular hexagon nut and can therefore be tightened to its maximum limit.
If the gap is less than 1 pitch, there may be a chance that sufficient locking effect will not be produced so please refrain from using HARDLOCK NUT with the bolt. (The same conditions apply for reuse.)
Use a torque wrench to tighten the Concave nut with the recommended torque set by HARDLOCK Industry Co., Ltd
Even after correctly tightening the Concave nut with the torque within the range of recommended tightening torque, there may remain a gap between the nuts due to the tolerance of bolt diameter.
When tightening the Concave nut on to the Convex nut, one side of the nuts will first come into contact, which gives an indication of sufficient locking effect (The Concave nut will slightly incline after the contact between the protrusion and the recess.)
By applying additional torque , the nuts will come into full contact . This state produces the ultimate locking effect of the HARDLOCK NUT, but further tightening may cause the breakage of bolt threads.
Standard materials and coatings
| Material | Coating |
|---|---|
| Class 4/low-carbon steel (JIS SS400 equivalent) | Electrogalvanized (trivalent chromate) |
| Hot-dip galvanized (HDZ35) | |
| Class 8/medium-carbon steel (JIS S45C) | Manganese Phosphate coating |
| Class 10/chromium molybdenum steel (JIS SCM435) | |
| A2/stainless steel (JIS SUS304 or equivalent) | Unplated/plain |
Dimension table (M16–M130)
| d | Pitch | Convex nut | Concave nut | Width across flats | e | Overall height | Rim dia. | Unit weight | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | m | m1 | s | ℓ | D | g | |||||
| Normal size | Coarse | Basic | Tolerance | Basic | Tolerance | Basic | Tolerance | Approx. | Approx. | Approx. | Approx. |
| M5 | 0.8 | 4 | +0.1 -0.15 | 4 | +0.5 -0.2 | 8 | 0 -0.2 | 9.2 | 7.2 | 9.2 | 1.9 |
| M6 | 1.0 | 5 | ±0.3 | 5 | 0 -0.3 | 10 | 0 -0.6 | 11.5 | 8.5 | 11.5 | 4 |
| M8 | 1.25 | 6.5 | 0 -0.58 | 6.5 | 0 -0.58 | 13 | 0 -0.7 | 15 | 10.8 | 15.0 | 8.9 |
| M10 | 1.5 | 8 | 0 -0.58 | 8 | 0 -0.58 | 17 | 0 -0.7 | 19.6 | 13.2 | 19.6 | 18 |
| M12 | 1.75 | 10 | 0 -0.58 | 9.3 | 0 -0.58 | 19 | 0 -0.8 | 21.9 | 16.0 | 21.9 | 26 |
| M16 | 2.0 | 13 | ±0.9 | 11 | 0 -0.7 | 24 | 0 -0.8 | 27.7 | 21.2 | 27.7 | 46 |
| M20 | 2.5 | 16 | ±0.9 | 14.5 | 0 -0.7 | 30 | 0 -0.8 | 34.6 | 26.7 | 34.6 | 93 |
| M22 | 2.5 | 18 | ±0.9 | 15.6 | 0 -1.2 | 32 | 0 -1.0 | 37 | 29.9 | 37.0 | 115 |
| M24 | 3.0 | 19 | ±0.9 | 17.6 | 0 -1.2 | 36 | 0 -1.0 | 41.6 | 32.4 | 41.6 | 183 |
| M27 | 3.0 | 21 | ±1.0 | 17.6 | 0 -1.2 | 41 | 0 -1.0 | 47.3 | 33.5 | 47.3 | 243 |
| M30 | 3.5 | 23 | ±1.0 | 18.6 | 0 -1.2 | 46 | 0 -1.0 | 53.1 | 36.5 | 53.1 | 312 |
The external dimensions conform to JIS B1181 (2004)/ISO 4032 standards, specifically in width across flats. The thread screw tolerance adheres to JIS B0209 (2001)/ISO 965 6H specifications. The overall height was modified in January 2014 to approximate the maximum height, considering significant tolerance.
Tightening torque table (M16–M130)
| Nominal size | Reference tightening torque for the convex nut (same as general hex nut) *70% of the bolt yield point | Recommended tightening torque for the concave nut | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 4 (SS400 or equivalent) | Class 8 (S45C) | Class 10 (SCM435) | A2/stainless steel (JIS SUS304 or equivalent) | Common to all (min.–max.) | |||
| 4.8 (320 N/mm²) | 8.8 (640 N/mm²) | 10.9 (900 N/mm²) | A2-50 | A2-70 | |||
| Trivalent chromate | HDZ35 | Manganese Phosphate coating | Plain | ||||
| M5 | 2.5 | – | – | – | 1.6 | 3.4 | 2–3 |
| M6 | 4.1 | – | – | – | 2.7 | 5.7 | 4–5 |
| M8 | 9.8 | 23 | 19.7 | 27.7 | 6.5 | 14 | 9–13 |
| M10 | 20 | 45 | 39 | 55 | 13 | 27 | 18–24 |
| M12 | 34 | 79 | 68 | 96 | 22 | 48 | 27–39 |
| M16 | 84 | 197 | 170 | 237 | 55 | 120 | 70–100 |
| M20 | 165 | 384 | 330 | 463 | – | – | 120–200 |
| M22 | 225 | 523 | 450 | 630 | – | – | 150–250 |
| M24 | 285 | 664 | 570 | 801 | – | – | 160–300 |
| M27 | 415 | 972 | 835 | 1,171 | – | – | 250–390 |
| M30 | 565 | 1,319 | 1,130 | 1,590 | – | – | 270–440 |
The tightening torque for the convex nut with HDZ35 is calculated on the basis of a torque coefficient of 0.35.
For the tightening torque of the A2/stainless steel convex nut, refer to the strength classification of the bolt used.
Because the proof load of the convex nut is the same as a general single nut, there is no unique torque value.
The concave nut can be tightened until contact with the convex nut even if the tightening torque exceeds the recommended maximum value because the torque coefficient varies depending on the surface roughness.
For HDZ concave nuts, tighten 50% more than the recommended torque value due to the high torque coefficient.
Kouei is Distributor/Agent of Hard Lock Nut
Other items of Hard Lock Nut
Request the quotation for Hard Lock Nut
Related Products
-

Tosei Sharyo T-50,TN-50 Series Caster
-

Chiyoda Tsusho 4/6/8/10/12-OOTC FUJI TEE CONNECTOR [METAL BODY]
-

Kitz T4T/T4L Type 400 3-Way Bronze Ball Valves (Standard Bore)
-

Chiyoda Seiki KR-120H/KR-120H-H (Primary pressure: 15.0 MPa or less / Adjusted pressure 2.0 to 12.0 MPa)
-

NK-6000 Jacket Type Flexible Hose
-

Nippon Daiya Valve KM200 type Stainless Steel High-Performance Butterfly Valves






