Suntest
Suntest GY Series GYPD Probe

Manufacturer: Suntest Co.,Ltd
Model: GYPD
Magnetostrictive Displaiacement Transducer
 Model GY Series are “Displacement Transducers” employing magnetostrictive phenomena, especially the Wiedemann effect. An ultra-sonic wave is generated by a moving magnet operating near a magnetostrictive wave guide on which the sonic wave propagates up to the head of the transducer.
Model GY Series are “Displacement Transducers” employing magnetostrictive phenomena, especially the Wiedemann effect. An ultra-sonic wave is generated by a moving magnet operating near a magnetostrictive wave guide on which the sonic wave propagates up to the head of the transducer.
The propagation time is precisely measured by state of the art technology and then the absolute displacement transducer is operational.
[ Principle ]
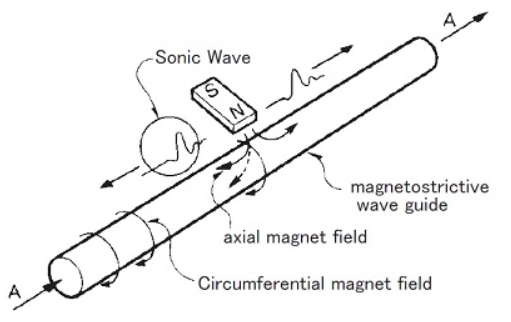
The figure shows the fundamental principle of operation.
When a current pulse like A is given to the wave guide, it generates a circumferential magnetic field on the wave guide, then placement of the movable magnet (polarized axially) as shown, only the axial magnetic field of the magnet affecting the wave guide produces a resultant field as indicated by the dotted line.
The vector combination of these two fields produces torsional strain, a phenomenon known as the Wiedemann Effect.
It is a form of vibration and propagates along the wave guide in the form of a transverse ultra-sonic wave.
The GY series displacement transducers detect the propagation time of the ultra-sonic wave.
GYPD Probe. ( Analogue / PWM / CANopen/SAEJ1939 )
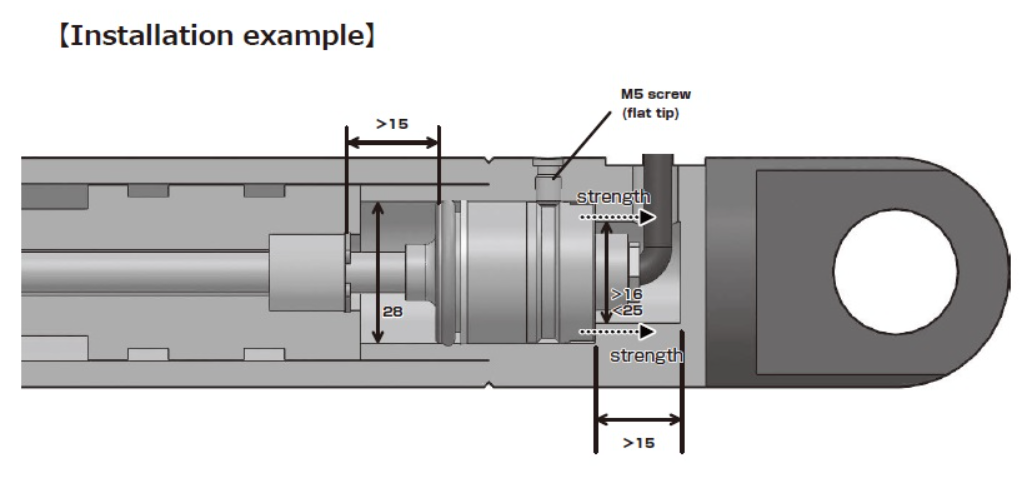
for built-in small hydraulic cylinder
 GYPD probe is the sensor for built-in hydraulic cylinder which has analogue output.
GYPD probe is the sensor for built-in hydraulic cylinder which has analogue output.
The sensor head is compact and the head dead zone is also short, so its total length becomes space saving.
With the dedicated software (GPM), zero and gain adjustment is possible at the user.
Output methods from sensors include analog (voltage/current) and PWM, CANopen methods.
We have also developed the SEA J1939 method as a new product.
Please contact us if you would like to use the SEA J1939 method.
Specifications
| Non-linearity | ≦±0.1mm(30〜250mm) ≦±0.04%FS(≧251mm) |
|---|---|
| Resolution | ≦0.06mm *CANopen:≦0.1mm |
| Repeatability | ≦±0.06mm *CANopen:≦±0.1mm |
| Temp.drift | ≦±0.006%FS/°C |
| Voltage output | 0.25〜4.75V or 0.5〜4.5V (load : Min.2kΩ) |
| Current output | 4〜20mA ( load : Max.250Ω ) |
| PWM output | 1kHz 5V 95〜5% ( load : Min.5kΩ ) |
| CANopen | CiA-301 ver. 4.2 / CiA-305 ver. 3.0.0 / CiA-406 ver. 4.2 |
| Power supply | +8〜36VDC (≦0.8W) |
| Sampling frequency | 4kHz (≦250mm) 2kHz (251〜500mm) 1kHz (≧501mm) |
| Max. Pressure | 45MPa ( continuous operating pressure ) |
| Operating temp. | -20°C〜+85°C |
| Storage temp. | -20°C〜+85°C |
| Vibration | 20G ( 5 〜 2000Hz ) |
| Shock | 100G ( 2msec ) |
| IP grade | IP67 |
(*): Changed the values for CANopen output. (20230208)
Model No.
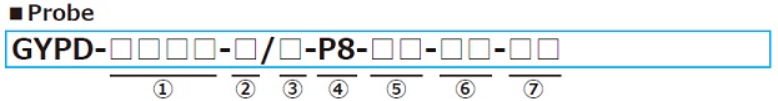
① Effective stroke
30mm-1000mm
② Head dead zone
15 : 15mm (Std.)
□ : □mm (option) ( specified by customers )
・Possible Min. length depends on the selected magnet.
③ Tip dead zone
70 : 70mm (Std.)
□ : □mm (option) ( specified by customers )
・Possible Min. length depends on the selected magnet.
④ Mount / Rod diameter
P8 : O-ring, rod Φ8(Std.)
⑤ Associated magnet
< magnet >
M3 : No.3
M0SM : No.ΦSPM
・Please consult if you select a magnet of other than above.
・This Model code means only specifying associated magnet.
・Ordering magnet individually
⑥ Cable connection
RG□F : pigtail / cable end : free
RG□A : pigtail / cable end : with connector for relay
( □ : cable length(m), Max.10m )(*)
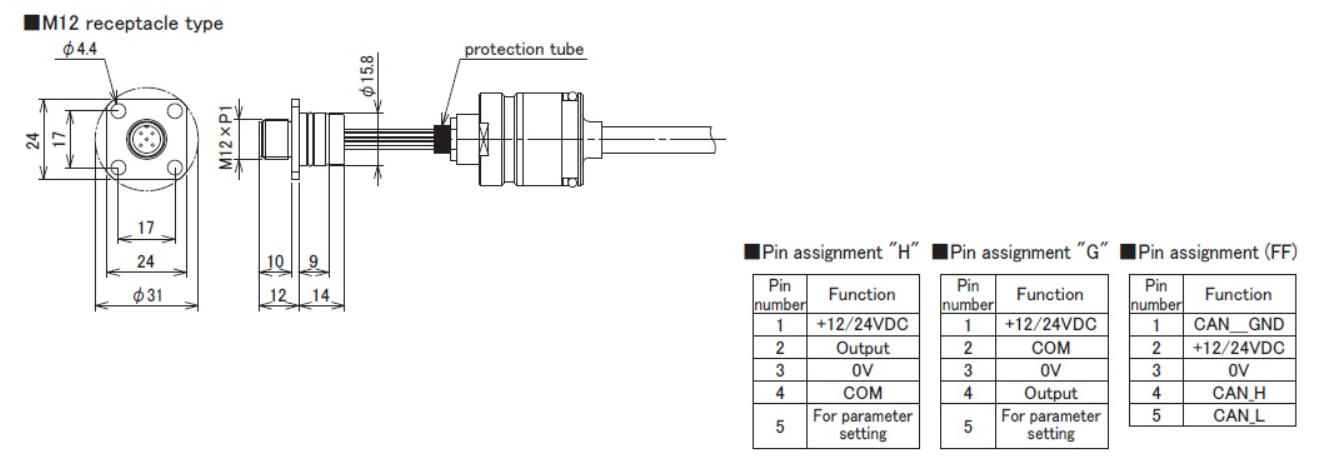
KV□△ : M12 receptacle type
□ : wire length (by 0.01m), Max.0.1m
△ : pin assignment( H: pin assignment “H”, G: pin assignment “G”,
FF: pin assignment “FF”)
(*) In case of using extension cable
Voltage output : sensor cable(m) + extension cable(m) ≦ 10m
Current output : sensor cable(m) + extension cable(m) ≦ 100m
PWM output : sensor cable (m) + extension cable (m) ≦ 10m
⑦ Position output
A1 : 0.25-4.75V ( When magnet moves toward tip, output increase. )
A2 : 4.75-0.25V( When magnet moves toward tip, output decrease. )
A3 : 0.5-4.5V( When magnet moves toward tip, output increase. )
A4 : 4.5-0.5V( When magnet moves toward tip, output decrease. )
BD : 4-20mA( When magnet moves toward tip, output increase. )
BR : 20-4mA( When magnet moves toward tip, output decrease. )
PWM1 : 1kHz 5V(5-95%)
PWM2 : 1kHz 5V(95-5%)
CO : CANopen
Dimensions
Probe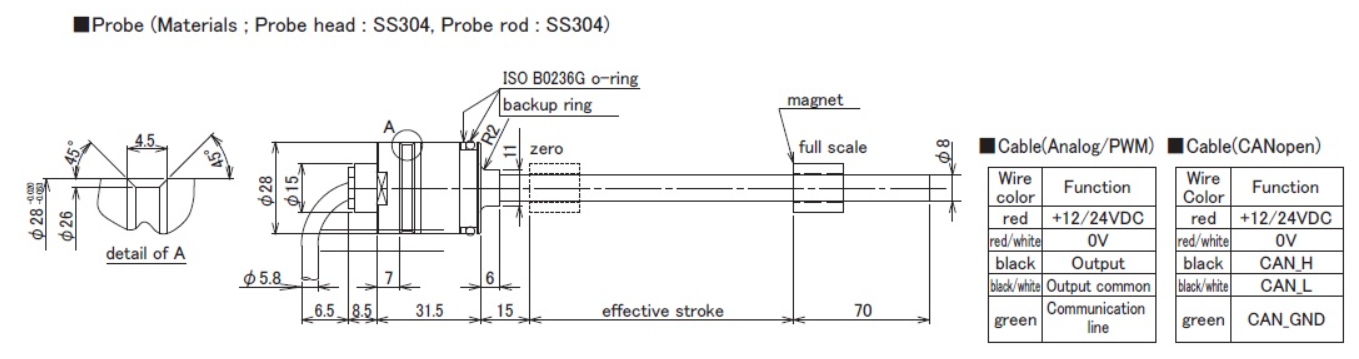
M12 receptacle
Application