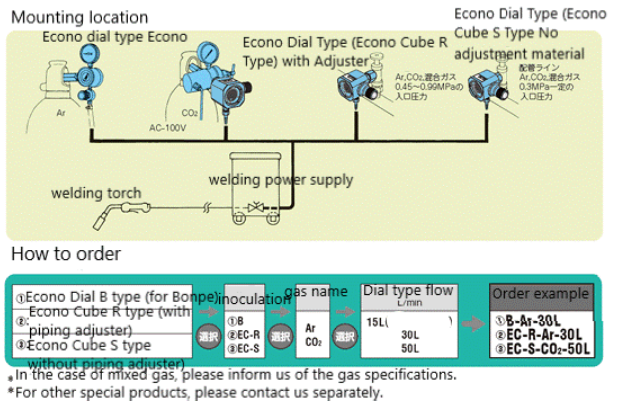
Chiyoda Seiki, Japan
Chiyoda Seiki B Type Series Gas Saver With Dial Type Flow Meter Econo Dial

Made in Japan
Manufacturer: Chiyoda Seiki
Model: B Type Series
With Heater For Carbon Dioxide Gas Cylinder
Feature
- This structure employs a balanced design that prevents secondary pressure fluctuations even if the container’s pressure drops.
- The pressure regulator is economical due to its unique structure that minimizes gas usage.
- Unlike the float-type flowmeter, the dial-type flowmeter can accurately return the flow rate regardless of the hose length.
- You can freely select the mounting angle because the flow rate remains consistent, regardless of the mounting angle.
- The easy-to-read scale allows you to accurately match the flow to the welding conditions.
- Gas Saver (Econoflow) offers easy operation with a simple left and right turn of the handle.
- It supplies a stable flow rate from the start of contacting, improving the arc start.
- It is rational and economical as there is no individual difference in gas consumption.
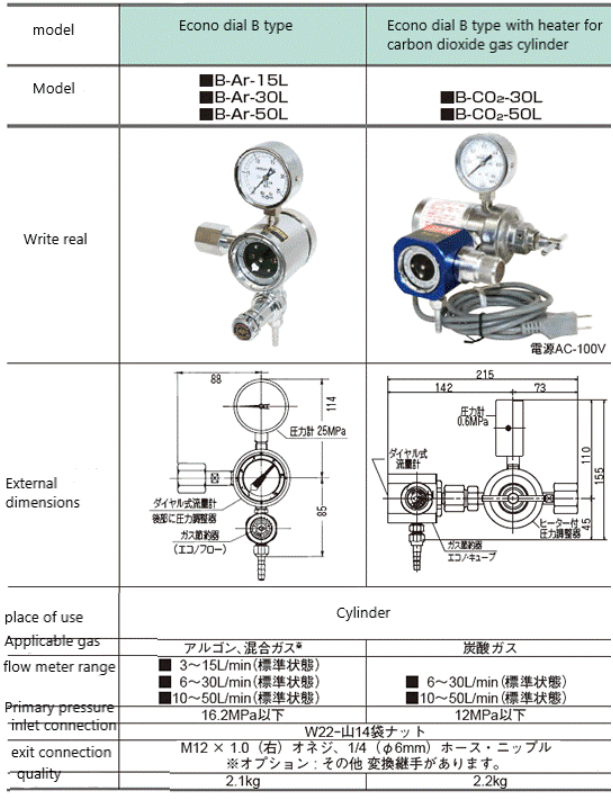
Specifications
Reasons for Saving Operation Principle of Gas Saver (Econoflo)
n conventional regulators with float type flow meters, the flow meter valve regulates the flow rate. When gas flows, the valve opening creates a differential pressure, making the downstream pressure lower than the upstream pressure. However, even when the outlet side is closed, and the gas flow stops, the valve remains “open” in the operating state, keeping the flow path unchanged. Consequently, the pressure inside the gas hose rises to the pressure gauge at the regulator’s outlet. This happens because the valve of the conventional float type flowmeter does not close the flow path.
Econoflow is a valve with a pressure adjustment function. In Econoflow, the adjustment handle sets the flow rate of the dial-type flow meter. When the gas stops, the inner diaphragm automatically rises, functioning as a stop valve and blocking the flow path while maintaining the adjusted working pressure, preventing the secondary pressure (internal pressure of the hose) from rising. As a result…Low pressure in hose.=The amount of gas remaining in the hose is small.=Less wasteful gas is emitted at the start.
=> Waste gas is greatly reduced in total, and shield gas cost can be greatly reduced.